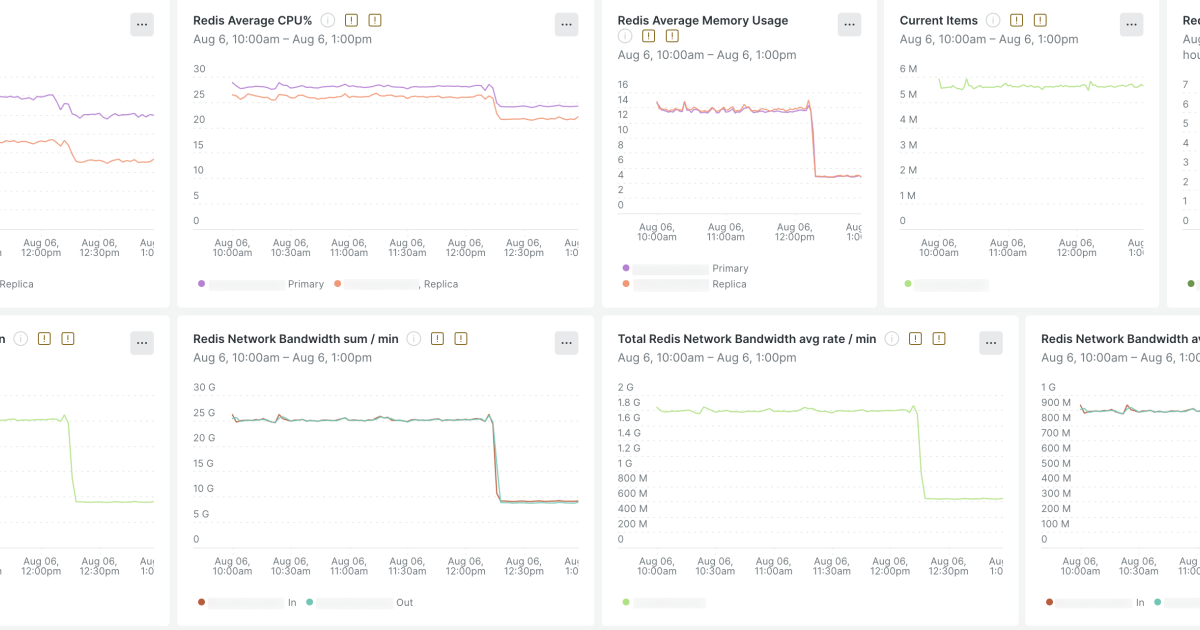
"Running observability at scale means handling massive streams of telemetry data including millions of spans, traces, and metrics every second. This data is what powers New Relic's ability to provide real-time insights into application and infrastructure performance for our customers. But ingesting and processing data in real-time at that scale comes with a price tag, especially when it involves high-performance systems like Redis that sit at the core of our distributed tracing pipeline."
"Our Distributed Tracing Pipeline team manages the system that ingest, transforms, connects and summarizes trace data from multiple agents. Last year, the team rolled out a new pipeline that simplified our overall architecture and reduced operational complexity. The redesign allowed us to deprecate older services, consolidate responsibilities into smaller, well-defined components, and most importantly, run both Infinite Tracing and standard distributed tracing through a single, unified pipeline."
Running observability at scale requires handling massive telemetry streams, including millions of spans, traces, and metrics every second. High-performance systems like Redis at the core of a distributed tracing pipeline generate significant storage and network costs. New Relic's Distributed Tracing Pipeline team redesigned the pipeline to simplify architecture, consolidate components, and unify Infinite Tracing with standard distributed tracing into a single pipeline, yielding a cleaner, more maintainable, and reliable system. Cost spikes triggered a two-part optimization: upgrading and right-sizing Redis clusters, then rethinking data storage to improve compression and memory efficiency. These measures cut Redis costs by more than half while improving performance and scalability.
Read at New Relic
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]