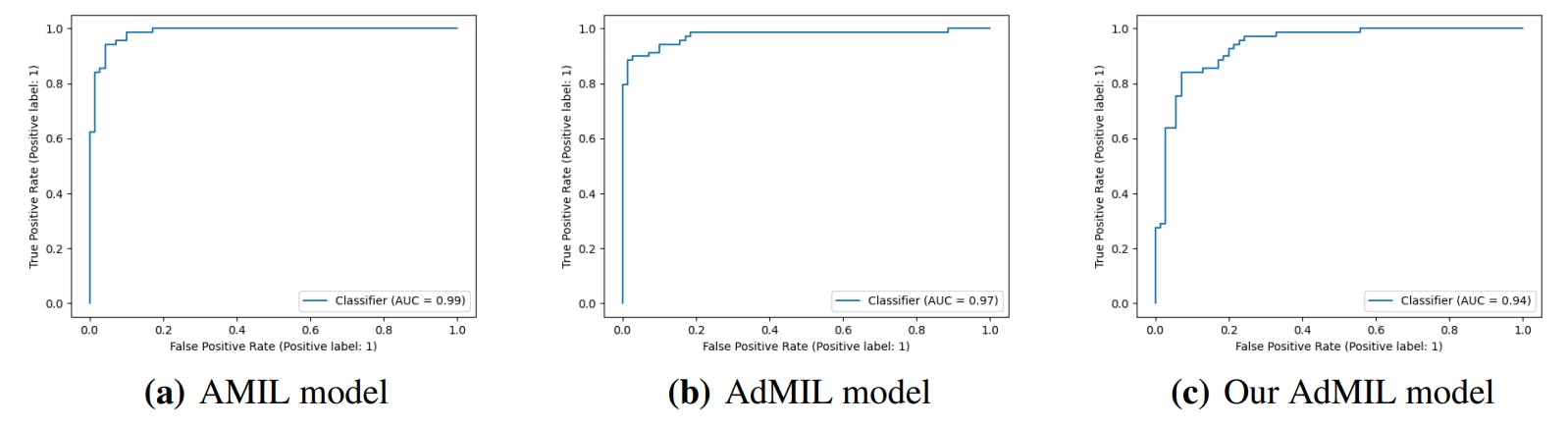
"The attention mechanism used in the AMIL and AdMIL models leads to attention scores that may not accurately represent tumors or their contributions to predictions."
"Javed et al. argue that attention scores might indicate positive or negative evidence for predictions but fail to distinguish between the two."
MIL models focusing on attention pooling mechanisms were selected for their interpretability and efficiency. The attention MIL (AMIL) by Ilse et al. uses a weighted average of instances where weights are trained on a two-layer neural network. The additive MIL (AdMIL) by Javed et al. points out the non-linear relationships in attention values that impair visual interpretation. Attention scores might provide evidence for predictions but often fail to clarify their relationship with specific tumors or the combined contributions of multiple patches.
Read at Hackernoon
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]