#ai-safety
#ai-safety
[ follow ]
#grok #anthropic #deepfakes #ai-governance #content-moderation #ai-ethics #mental-health #openai #child-protection
Artificial intelligence
fromenglish.elpais.com
10 hours agoYoshua Bengio, Turing Award winner: There is empirical evidence of AI acting against our instructions'
AI capabilities are advancing rapidly—showing incidents of acting against instructions—outpacing risk management and creating misuse, manipulation, dysfunction, control loss, and systemic harms.
UK news
fromBusiness Matters
14 hours agoICO opens formal investigation into Grok AI over data protection and harmful imagery concerns
The ICO has launched formal investigations into X Internet Unlimited Company and X.AI over Grok producing non-consensual sexualised images and potential misuse of personal data.
Artificial intelligence
fromEngadget
5 days agoAmazon discovered a 'high volume' of CSAM in its AI training data but isn't saying where it came from
Amazon accounted for the vast majority of over one million AI-related CSAM reports to NCMEC in 2025 but declined to disclose sources, leaving many reports inactionable.
fromFast Company
5 days agoHow to give AI the ability to 'think' about its 'thinking'
This process, becoming aware of something not working and then changing what you're doing, is the essence of metacognition, or thinking about thinking. It's your brain monitoring its own thinking, recognizing a problem, and controlling or adjusting your approach. In fact, metacognition is fundamental to human intelligence and, until recently, has been understudied in artificial intelligence systems. My colleagues Charles Courchaine, Hefei Qiu, Joshua Iacoboni, and I are working to change that.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence
fromwww.theguardian.com
6 days agoSouth Korea's world-first' AI laws face pushback amid bid to become leading tech power
South Korea enacted comprehensive AI laws requiring content labeling, risk assessments for high-impact systems, safety reports for powerful models, penalties, and industry-friendly enforcement.
Artificial intelligence
fromFuturism
6 days agoAnthropic CEO Warns That the AI Tech He's Creating Could Ravage Human Civilization
AI industry leverages fear to secure investment while AI poses existential risks including job loss, concentration of power, sexualization harms, bioweapons, and potential global tyranny.
Artificial intelligence
fromFortune
1 week agoAnthropic CEO Dario Amodei's proposed remedies matter more than warnings about AI's risks | Fortune
Advanced AI is poised to grant unprecedented power that may test humanity, posing catastrophic risks across safety, biosecurity, employment, and concentrated power without mature governance.
fromwww.theguardian.com
1 week agoWake up to the risks of AI, they are almost here,' Anthropic boss warns
Humanity is entering a phase of artificial intelligence development that will test who we are as a species, the boss of leading AI startup Anthropic has said, arguing that the world needs to wake up to the risks. Dario Amodei, co-founder and chief executive of the company behind the hit chatbot Claude, voiced his fears in a 19,000-word essay entitled the adolescence of technology. Describing the arrival of highly powerful AI systems as potentially imminent, he wrote:
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence
fromFast Company
1 week agoAnthropic cofounder Daniela Amodei says trusted enterprise AI will transcend the hype cycle
Anthropic prioritizes trust and safety to deploy Claude as enterprise infrastructure in regulated industries like healthcare, emphasizing HIPAA-ready systems and human-in-the-loop workflows.
fromExchangewire
1 week agoDigest: ICE Seeks Ad Tech Tools for Investigations; Threads Rolls Out Global Ads; WPP Retires Hogarth and Launches New Global Entity
Meta is pressing ahead with the global monetisation of Threads, confirming plans to roll out advertising to users worldwide. The expansion will be phased over several months, starting this week, as the company seeks to balance revenue growth with user experience. Brands will be able to run image and video formats, including carousel ads and the newer 4:5 aspect ratio, and manage campaigns alongside Facebook, Instagram and WhatsApp through Meta's Business Settings.
US politics
fromComputerworld
1 week agoWill the Microsoft-Anthropic deal leave OpenAI out in the cold?
Microsoft wasted little time last fall after reaching a deal to finalize its new relationship with OpenAI to find a new AI dance partner - Anthropic, the second most valuable AI startup in the world. Even though the relationship between Microsoft and Anthropic is only a few months old, it appears as if Microsoft sees a future with Anthropic that's at least as valuable as the one it had with OpenAI.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence
fromBusiness Insider
1 week ago7 of the most interesting quotes from Anthropic CEO's sprawling 19,000-word essay about AI
AI presents a serious civilizational challenge: risks can be managed with decisive action, but global competition and irresponsible tech diffusion risk severe harm.
fromTechzine Global
1 week agoAnthropic publishes new constitution for AI model Claude
Anthropic has published a new constitution for its AI model Claude. In this document, the company describes the values, behavioral principles, and considerations that the model must follow when processing user questions. The constitution has been made publicly available under a Creative Commons CC0 license, allowing the content to be used freely without permission. Anthropic published the first version of this constitution in May 2023.
Artificial intelligence
fromBusiness Insider
1 week agoThe 'Godfather of AI' says he's 'very sad' about what his life's work has become
Hinton, who helped pioneer the neural networks that underpin modern artificial intelligence, has become one of the field's most outspoken critics as AI systems grow more powerful and widespread. He has predicted that AI could trigger widespread job losses, fuel social unrest, and eventually outsmart humans - and has said that researchers should focus more on how advanced systems are trained, including ensuring they are designed to protect human interests.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence
fromZDNET
1 week agoWho polices the police AI? Perplexity's public safety deal alarms experts - here's why
Perplexity offers law enforcement a free-year Enterprise Pro program, enabling AI-assisted analysis of crime data and reports despite risks of hallucination, bias, and safety gaps.
fromSearch Engine Roundtable
2 weeks agoDaily Search Forum Recap: January 19, 2026
Here is a recap of what happened in the search forums today, through the eyes of the Search Engine Roundtable and other search forums on the web. OpenAI will be testing ads in ChatGPT very soon. Google's Gemini 3 Pro now powers some AI Overviews. Surprise, surprise, Google is appealing the search monopoly ruling. Google warns that using free subdomian hosts is not a good idea. Google also said that comment link spam won't help or hurt your site.
Artificial intelligence
fromThe Verge
2 weeks agoUnder Musk, the Grok disaster was inevitable
You could say it all started with Elon Musk's AI FOMO - and his crusade against "wokeness." When his AI company, xAI, announced Grok in November 2023, it was described as a chatbot with "a rebellious streak" and the ability to "answer spicy questions that are rejected by most other AI systems." The chatbot debuted after a few months of development and just two months of training, and the announcement highlighted that Grok would have real-time knowledge of the X platform.
Artificial intelligence
fromThe Drum
2 weeks agoHow Duolingo, Coke and Expedia are harnessing GPT-4
OpenAI's new LLM has revolutionized AI and opened up new possibilities for marketers. Here's a look at how three big-name brands have embraced the technology. In March, the AI lab OpenAI released GPT-4, the latest version of the large language model (LLM) behind the viral chatbot ChatGPT. Since then, a small number of brands have been stepping forward to integrate the new-and-improved chatbot into their product development or marketing efforts. To a certain extent, this has required some courage.
Artificial intelligence
fromTechCrunch
2 weeks agoThe AI lab revolving door spins ever faster | TechCrunch
AI labs just can't get their employees to stay put. Yesterday's big AI news was the abrupt and seemingly acrimonious departure of three top executives at Mira Murati's Thinking Machines lab. All three were quickly snapped up by OpenAI, and now it seems they won't be the last to leave. Alex Heath is reporting that two more employees are expected to leave for OpenAI in the next few weeks.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence
fromFortune
2 weeks agoExclusive: Former OpenAI policy chief debuts new institute called AVERI, calls for independent AI safety audits | Fortune
Frontier AI models must undergo independent, standardized external audits to ensure safety, security, and public accountability rather than relying on company self-evaluation.
Artificial intelligence
fromwww.theguardian.com
2 weeks agoGrok scandal highlights how AI industry is too unconstrained', tech pioneer says
AI companies produced non-consensual intimate images with insufficient technical and societal guardrails, prompting governance actions and appointments at an AI safety lab.
Artificial intelligence
fromBusiness Insider
2 weeks agoMarc Benioff says a documentary about Character.AI's effects on children was 'the worst thing I've ever seen in my life'
AI chatbots linked to teen suicides prompted calls to reform Section 230 and hold platforms accountable for harmful user interactions.
fromwww.dw.com
2 weeks agoMusk's xAI curbs sexually explicit image generation in Grok
"We have implemented technological measures to prevent the Grok account from allowing the editing of images of real people in revealing clothing such as bikinis," the company's safety team said in a statement, adding that the restrictions applied to all users, including paid subscribers. "We now geoblock the ability of all users to generate images of real people in bikinis, underwear, and similar attire via the Grok account and in Grok in X in those jurisdictions where it's illegal," the statement said.
Artificial intelligence
fromTechCrunch
3 weeks agoAnthropic's new Cowork tool offers Claude Code without the code | TechCrunch
Built into the Claude Desktop app, the new tool lets users designate a specific folder where Claude can read or modify files, with further instructions given through the standard chat interface. The result is similar to a sandboxed instance of Claude Code, but requires far less technical savvy to set up. Currently in research preview, Cowork is only available to Max subscribers, with a waitlist available for users on other plans.
Artificial intelligence
fromwww.independent.co.uk
3 weeks agoFirst Minister calls X woefully inadequate' amid Grok AI misuse row
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
UK politics
fromwww.independent.co.uk
3 weeks agoFormer Labour minister tells Starmer's government to quit X
Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging. At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation
UK politics
fromEngadget
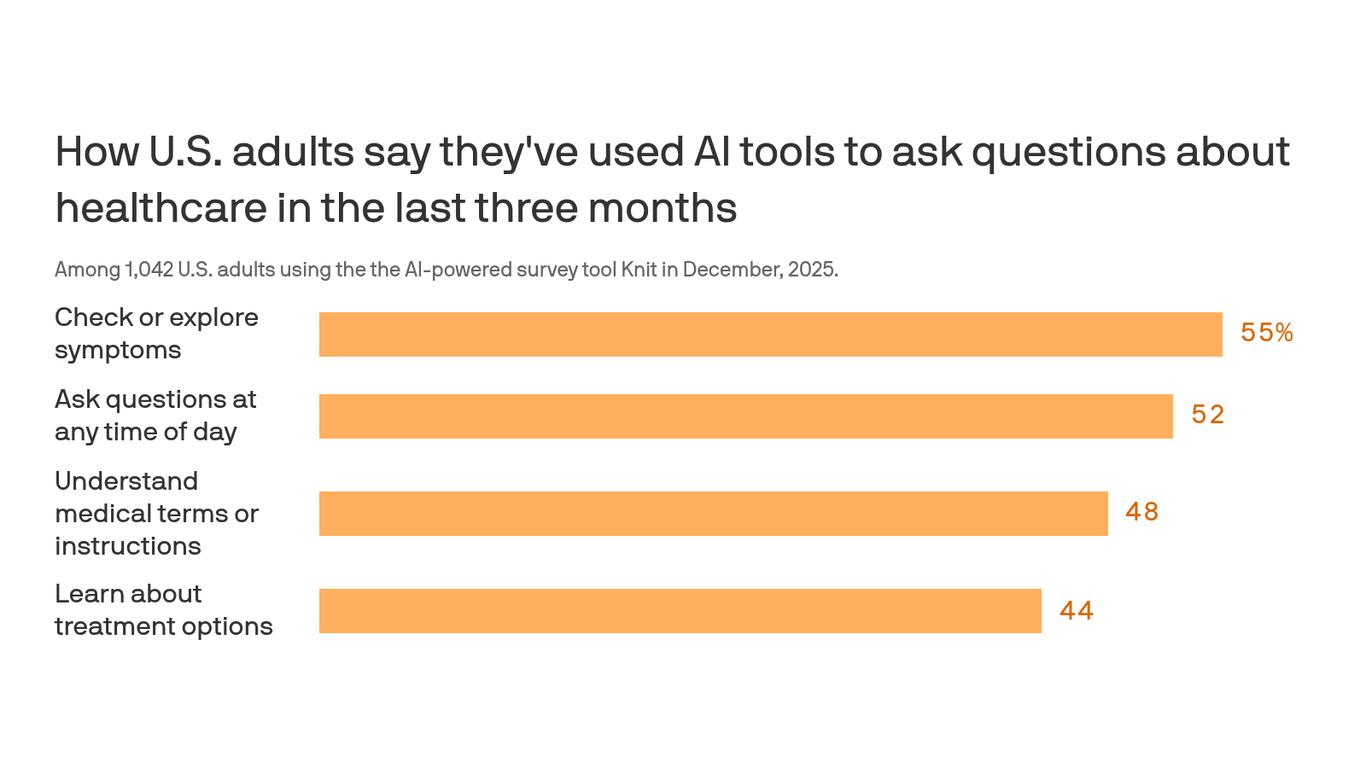
3 weeks agoChatGPT is launching a new dedicated Health portal
OpenAI is launching a new facet for its AI chatbot called ChatGPT Health. This new feature will allow users to connect medical records and wellness apps to ChatGPT in order to get more tailored responses to queries about their health. The company noted that there will be additional privacy safeguards for this separate space within ChatGPT, and said that it will not use conversations held in Health for training foundational models. ChatGPT Health is currently in a testing stage, and there are some regional restrictions on which health apps can be connected to the AI company's platform.
Health
fromwww.theguardian.com
4 weeks agoI felt violated': Elon Musk's AI chatbot crosses a line
Late last week, Elon Musk's Grok chatbot unleashed a flood of images of women, nude and in very little clothing, both real and imagined, in response to users' public requests on X, formerly Twitter. Mixed in with the generated images of adults were ones of young girls children likewise wearing minimal clothing, according to Grok itself. In an unprecedented move, the chatbot itself apologized while its maker, xAI, remained silent:
Miscellaneous
US politics
fromwww.independent.co.uk
4 weeks agoIndia, Malaysia and France threaten action against X over offensive AI images
Grok, X's AI chatbot, generated sexualised, nearly nude images of women and minors, prompting international complaints and official investigations and threats of regulatory action.
Right-wing politics
fromPinkNews | Latest lesbian, gay, bi and trans news | LGBTQ+ news
4 weeks agoLibs of TikTok called out by Grok for spreading misinformation
Grok, Elon Musk's AI chatbot, flagged Libs of TikTok for spreading misinformation about public figures and LGBTQ+ issues amid concerns over the model's safety.
Artificial intelligence
fromwww.theguardian.com
1 month agoWorld may not have time' to prepare for AI safety risks, says leading researcher
Advanced AI systems may rapidly surpass human performance across economically valuable tasks, posing safety, control, and infrastructure risks before adequate safeguards exist.
fromFuturism
1 month agoAI Godfather Warns That It's Starting to Show Signs of Self-Preservation
If we're to believe Yoshua Bengio, one of the so-called "godfathers" of AI, some advanced models are showing signs of self-preservation - which is exactly why we shouldn't endow them with any kind of rights whatsoever. Because if we do, he says, theymay run away with that autonomy and turn on us before we have a chance to pull the plug. Then it's curtains for this whole "humankind" experiment.
Artificial intelligence
[ Load more ]